1.认证
- 创建类,继承BaseAuthentication,实现:authenticate方法
- 返回值有三种:
- 返回None,下一个认证执行
- 抛出异常,raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(‘msg’),通常会有两种可能的返回值
- 401 Unauthorized 未认证;
- 403 Permission Denied 权限被禁止(配合权限使用)。
- 返回一个元组(user,auth)
通常,可以在设置文件中配置全局使用的认证方案
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
)
}
|
同样也可局部使用,为不同的视图分别指定不同的认证方案,此时可在视图中通过 authentication_classes指定
1
2
3
4
5
| from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class XXXView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication]
|
认证的源码流程
请求进来走dispatch
initialize_request封装request
get_authenticators:获取定义的认证类,通过列表推导式创建对象
initial:perform_authentication里返回request.user(内部循环)
项目中通常使用的认证方式:jwt认证方式
2.权限
- 创建类,继承BasePermission,必须实现has_permission方法 -
- 返回值两种:TRUE或者FALSE
权限功能的使用
权限控制可以限制用户对于视图的访问和对于具体数据对象的访问。
通常,可以在设置文件中配置全局使用的权限管理方案
1
2
3
4
5
6
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
)
}
|
与认证类似,也可以在视图中通过 permission_classes 属性来设置权限类,如
1
2
3
4
5
| from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class XXXView(APIView):
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated,MyPermission]
|
Django Rest framework为我们提供的权限:
- AllowAny:允许所有用户;
- IsAuthenticated:仅通过认证的用户;
- IsAdminUser:仅管理员用户;
- IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly:认证的用户可以完全操作(增删改查),否则只能读取(查)。
自定义权限
Django Rest framework 为我们提供的权限具有局限性,有时无法满足实际需求,此时需要自定义权限,只需继承 rest_framework.permissions.BasePermission,并重写以下两个方法:
.has_permission(self, request, view)
是否可以访问视图, view表示当前视图对象
.has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj)
是否可以访问数据对象, view表示当前视图, obj为数据对象
例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
class MyPermission(BasePermission):
message = '无权访问'
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user:
return True
return False
def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
"""控制对obj对象的访问权限,我们此时
判断用户请求是否为安全请求SAFE_METHODS = ('GET', 'HEAD', 'OPTIONS')
否则返回False,拒绝任何人的请求"""
if request.method in permissions.SAFE_METHODS:
return True
return False
class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated, MyPermission]
|
3.限流
作用:
为了防止恶意访问,或减轻服务器压力,我们需要对用户的访问频率进行限制。在配置文件中,使用DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES 和 DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES进行全局配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.throttling.AnonRateThrottle',
'rest_framework.throttling.UserRateThrottle'
),
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'anon': '100/day',
'user': '1000/day'
'xxx':'2/minute'
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle
class AnonThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'xxx'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
if request.user:
return None
return self.get_ident(request)
from rest_framework.throttling import UserRateThrottle
class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
authentication_classes = [SessionAuthentication]
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated]
throttle_classes = [UserRateThrottle]
|
Django Rest framework为我们提供的限流类
限制用户对于每个视图的访问频次,使用 ip 或 user id 区分不同用户。
例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class ContactListView(APIView):
throttle_scope = 'contacts'
class ContactDetailView(APIView):
throttle_scope = 'contacts'
class UploadView(APIView):
throttle_scope = 'uploads'
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.throttling.ScopedRateThrottle',
),
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'contacts': '1000/day',
'uploads': '20/day'
}
}
|
4.过滤
Django Rest framework中,可以使用 django-fitlter 来实现过滤功能。在使用该功能前,需要提前安装和注册 django-filter。
在终端完成 django-filter 的安装:
1
| pip install django-filter
|
在配置文件中配置以下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django_filters',
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': ('django_filters.rest_framework.DjangoFilterBackend',)
}
|
在视图中添加 filter_fields 属性,指定可以过滤的字段:
1
2
3
4
| class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
filter_fields = ('age')
|
通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/students/?age=18来获取成年的学生信息。
5.排序
在类视图中设置 filter_backends,使用rest_framework.filters.OrderingFilter过滤器,REST framework 会在请求的查询字符串参数中检查是否包含了 ordering 参数,如果包含了 ordering 参数,则按照 ordering 参数指明的排序字段对数据集进行排序。
前端可以传递的 ordering 参数的可选字段值需要在 ordering_fields 中指明。
1
2
3
4
5
| class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
filter_backends = [OrderingFilter]
ordering_fields = ('id', 'age', 'number')
|
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/students/?ordering=-age ,服务器返回按年龄逆序排序后的学生信息。
6.分页
在进行条件查询的时候往往不确定数量的多少,如果数量过大,一次性返回所有数据,会使服务器承受巨大的压力,以分页的方式提供数据,相当于将庞大的数据打散,每次只按要求返回一定数量的数据,就可以减轻服务器压力。
全局配置分页
1
2
3
4
5
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination',
'PAGE_SIZE': 10
}
|
也可通过自定义 Pagination 类,来为视图添加不同分页行为。在视图中通过pagination_class 来指明。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| class LargeResultsSetPagination(PageNumberPagination):
page_size = 10
page_size_query_param = 'page_size'
max_page_size = 1000
class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
pagination_class = LargeResultsSetPagination
|
注意:如果需要关闭分页功能,只需在视图内设置
1
2
| pagination_class = None
|
自定义分页器
如果默认的分页功能无法满足要求,可以自行定义分页器。
前端访问网址形式:
1
2
| GET http://127.0.0.1/api/students/?page=4
|
可以在子类中定义的属性:
- page_size :每页数目;
- page_query_param :前端发送的页数关键字名,默认为”page”;
- page_size_query_param :前端发送的每页数目关键字名,默认为None;
- max_page_size :前端最多能设置的每页数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination
class StandardPageNumberPagination(PageNumberPagination):
page_size_query_param = 'page_size'
max_page_size = 10
class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
pagination_class = StandardPageNumberPagination
|
前端访问网址形式:
1
2
| GET http://127.0.0.1/api/students/?limit=100&offset=400
|
可以在子类中定义的属性:
- default_limit: 默认限制,默认值与
PAGE_SIZE设置为一致;
- limit_query_param limit:参数名,默认 ‘limit;
- offset_query_param: offset 参数名,默认 ‘offset’;offset(偏移量)
- max_limit :最大 limit 限制,默认 None。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| from rest_framework.pagination import LimitOffsetPagination
class StudentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = StudentsModel.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentsSerializer
pagination_class = LimitOffsetPagination
|
7.版本
全局配置
1
2
3
4
5
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'VERSION_PARAM':'version',
'DEFAULT_VERSION':'v1',
'ALLOWED_VERSIONS':['v1','v2'], 'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS':"rest_framework.versioning.URLPathVersioning" }
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from django.conf.urls import url,include
from django.contrib import admin
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^api/(?P<version>[v1|v2]+)/', include('api.urls'), name='users-list'),
]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class UserView1(APIView):
versioning_class = URLPathVersioning
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
print(request.version)
print(request.versioning_scheme)
if request.version=='v1':
return Response('我是版本一')
elif request.version=='v2':
return Response('我是版本二')
else:
return Response('默认')
|
8.异常处理
当遇到异常时,Django Rest framework 会自动捕获,并按默认逻辑处理。也可以通过自定义异常处理函数来实现对异常的处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| from rest_framework.views import exception_handler
def custom_exception_handler(exc, context):
response = exception_handler(exc, context)
if response is not None:
response.data['status_code'] = response.status_code
return response
|
在配置文件中声明自定义的异常处理
1
2
3
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'my_project.my_app.utils.custom_exception_handler'
}
|
如果未声明,会采用默认的方式,如下
1
2
3
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler'
}
|
例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| from rest_framework.views import exception_handler
from django.db import DatabaseError
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import status
from redis import RedisError
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger('django')
def custom_exception_handler(exc, context):
"""
自定义异常处理
:param exc: 异常类
:param context: 抛出异常的上下文
:return: Response响应对象
"""
response = exception_handler(exc, context)
if response is None:
view = context['view']
if isinstance(exc, DatabaseError):
logger.error('[%s] %s' % (view, exc))
response = Response({'message': '服务器内部错误'}, status=status.HTTP_507_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE)
if isinstance(exc, RedisError):
logger.error('[%s] %s' % (view, exc))
response = Response({'message': '服务器内部错误'}, status=status.HTTP_507_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE)
return response
|
REST framework 提供的异常类
- APIException 所有异常的父类;
- ParseError 解析错误;
- AuthenticationFailed 认证失败;
- NotAuthenticated 尚未认证;
- PermissionDenied 权限决绝;
- NotFound 未找到;
- MethodNotAllowed 请求方式不支持;
- NotAcceptable 要获取的数据格式不支持;
- Throttled 超过限流次数;
- ValidationError 校验失败。
9.日志
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
LOGGING = {
'version': 1,
'disable_existing_loggers': False,
'formatters': {
'verbose': {
'format': '%(levelname)s %(asctime)s %(module)s %(lineno)d %(message)s'
},
'simple': {
'format': '%(levelname)s %(module)s %(lineno)d %(message)s'
},
},
'filters': {
'require_debug_true': {
'()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugTrue',
},
},
'handlers': {
'console': {
'level': 'DEBUG',
'filters': ['require_debug_true'],
'class': 'logging.StreamHandler',
'formatter': 'simple'
},
'file': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler',
'filename': os.path.join(os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR), "logs/renran.log"),
'maxBytes': 300 * 1024 * 1024,
'backupCount': 10,
'formatter': 'verbose'
},
},
'loggers': {
'django': {
'handlers': ['console', 'file'],
'propagate': True,
},
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
| import logging
logger = logging.getLogger('django')
logger.error('')
|
10.接口文档
在前后端分离的项目中,在完成接口的开发之后,后端开发人员需要为前端人员编写接口文档,介绍接口调用方法和需要传递的参数。在 Django Rest framework 编写接口后,可以自动生成接口文档,以网页的方式呈现
安装依赖
Django Rest framework 自动生成接口文档,需要coreapi库的支持
在设置文件中进行配置
1
2
3
| REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.AutoSchema'
}
|
配置接口文档访路由地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
| from rest_framework.documentation import include_docs_urls
urlpatterns = [
...
path('docs/', include_docs_urls(title='接口文档'))
]
|
文档描述说明的定义位置
单一方法的视图,可直接使用类视图的文档字符串,如:
1
2
3
4
| class StudentView(generics.ListAPIView):
"""
返回所有学生信息.
"""
|
包含多个方法的视图,在类视图的文档字符串中,分开方法定义,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class StudentListCreateView(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
"""
get:
返回所有学生信息.
post:
新建学生信息.
"""
|
对于视图集 ViewSet,仍在类视图的文档字符串中分开定义,但是应使用操作动作名称来区分,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class BookInfoViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin, mixins.RetrieveModelMixin, GenericViewSet):
"""
list:
返回学生列表数据
retrieve:
返回学生详情数据
latest:
返回最新的学生数据
"""
|
访问接口文档网页
浏览器访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs/,即可看到自动生成的接口文档 。
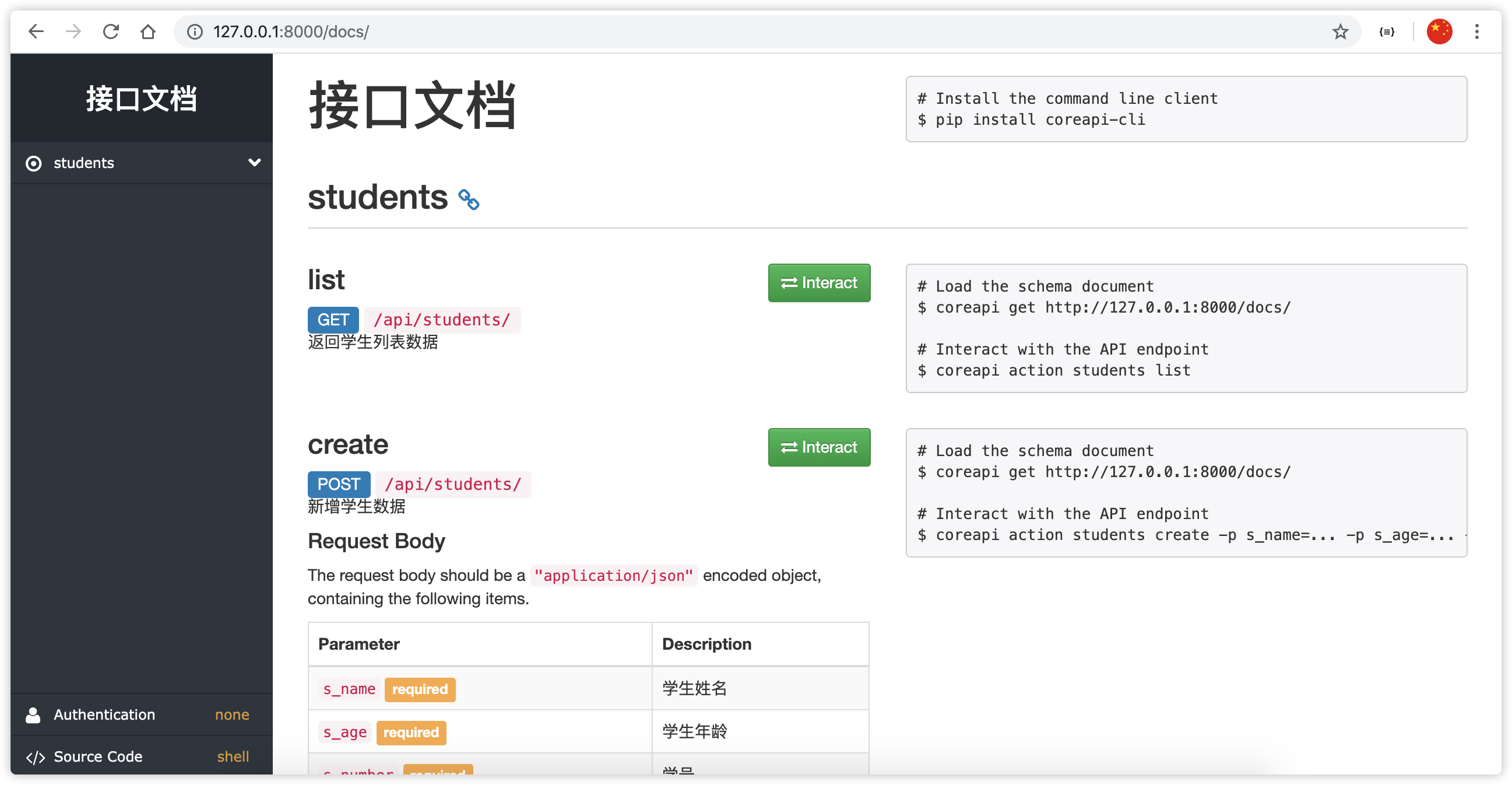
注意:
- 视图集 ViewSet 中的 retrieve 方法,在接口文档中被称作 read;
- 参数的 Description 需要在模型类或序列化器类的字段中以 help_text 选项定义,如:
1
2
3
| class StudentsModel(models.Model):
...
name = models.CharField(max_length=8, verbose_name='学生姓名', help_text='学生姓名')
|



